Select:
Periodontology
Periodontics is the field of dentistry that deals with the treatment and prevention of periodontitis , in all its forms , acute , chronic and aggressive . The symptoms of this disease are gum redness (gingivitis), bleeding , halitosis, probing ( formation of "pockets" where bacteria can breed freely, perpetuating [keeping on] the inflammatory process ) and in later stages abscesses and tooth mobility , ending up in teeth loss.
Periodontitis not only attacks soft tissues, but at an advanced stage it is also characterized by resorption of the bone around the teeth with consequent loosening.
The rate of periodontitis is very high; it is estimated that it affects 60% of the population in Italy, increasing in progression with ageing.
There are also particularly aggressive forms affecting young patients (10-14 %) that must be blocked at an early stage.
Non specialists often neglects the diagnosis of periodontitis: the study of intra-oral x-rays slabs made tooth by tooth ( status x-ray ) and periodontal probing ( mapping periodontal pockets ) are essential to make a proper diagnosis and correctly conjecture on the prognosis for the disease .
Etiology , that is the cause of the disease, is bacterial (presence of dental plaque) and its treatment consists in the removal of plaque and calculus above and below the gum by accurate dental hygiene sessions, during which the patient will also be shown the correct use of all tools available for proper control of dental plaque.
Periodontitis is also associated with a certain familiarity (predisposing genetic factors in addition to the exposure to pathogens within the same household) and is favored by conditions such as immune deficiencies , diabetes and some drugs that cause gingival hypertrophy (cyclosporine and calcium channel blockers ).
Smoking in all its forms is strongly implicated as a risk factor favoring the development of periodontitis, in relation to number of cigarettes and exposure time. In addition to being linked to cardiovascular diseases , and especially broncopneumatiche oncological diseases , smoke acts locally on the oral mucous membranes by inhibiting immunity against pathogens (inhibition of phagocytosis and chemotaxis of neutrophils, inhibition of antibody production ), it favors autoimmune mechanisms ( increased release by of macrophages of IL- 1 and TNF - α ) , it has a vasoconstrictive action on the microcirculation and during gingival healing processes it inhibits both the vascularization and fibroblasts and osteoblasts synthesis activity. The low oxygen partial tension in the oral environment (oral cavity) observed in patients who smoke also favors the development of pathogenic forms associated with periodontitis (A. actinomycetemcomitans, T. forsythia e P. gingivalis).
Treatment of periodontitis can include making surgical flaps that allow a very visible access to all portions of the dental root, which is especially important in case of vertical flaws, that means deep and narrow. In that case, you can use amelogenin to achieve unexpected healings.
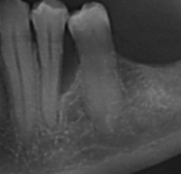
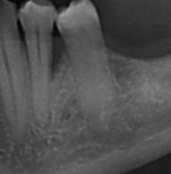
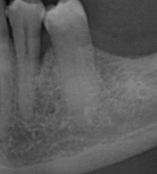
Other surgical flaps, such as “flap in apical position”, are more suitable for rear areas and for those areas that have to be rehabilitated with prosthetic.
Unfortunately, if periodontitis is already at an advanced stage with an high grade of tooth mobility, teeth will need to be solidarized between them by splinting or temporary prosthetic BEFORE the surgical phase : not abiding by this simple rule would result in bone loss you would otherwise have been able to keep, and the therapy will fail.
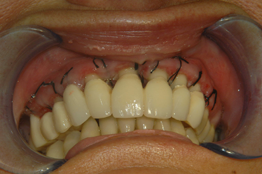
Once the acute inflammatory process of periodontitis has been stopped, restoring a maintainable periodontal and dental anatomy can not be left out of consideration: the presence of damaged furcations, bone hollows , partially edentulous areas , are not compatible with a long-term maintenance.
Patients who received a periodontal rehabilitation will be included into operational protocols that provide for frequent professional hygiene sessions first, that decrease in frequency as the situation is made fixed.